glasses.models.classification package¶
Subpackages¶
- glasses.models.classification.alexnet package
- glasses.models.classification.base package
- glasses.models.classification.deit package
- glasses.models.classification.densenet package
- glasses.models.classification.efficientnet package
- glasses.models.classification.fishnet package
- glasses.models.classification.mobilenet package
- glasses.models.classification.regnet package
- glasses.models.classification.resnest package
- glasses.models.classification.resnet package
- glasses.models.classification.resnetxt package
- glasses.models.classification.senet package
- glasses.models.classification.vgg package
- glasses.models.classification.vit package
- glasses.models.classification.wide_resnet package
Module contents¶
Classification models
- class glasses.models.classification.AlexNet(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.alexnet.AlexNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.alexnet.AlexNetHead'>, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.base.ClassificationModuleImplementation of AlexNet proposed in ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks, according to the variation implemented in torchvision.
net = AlexNet()
Examples
# change activation AlexNet(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) AlexNet(n_classes=100) # pass a different block AlexNet(block=SENetBasicBlock)
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Default is 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Default is 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.DeiT(*args, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.deit.DeiTClassificationHead'>, tokens: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.deit.DeiTTokens'>, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.vit.ViTImplementation of DeiT proposed in Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention
An attention based distillation is proposed where a new token is added to the model, the dist token.
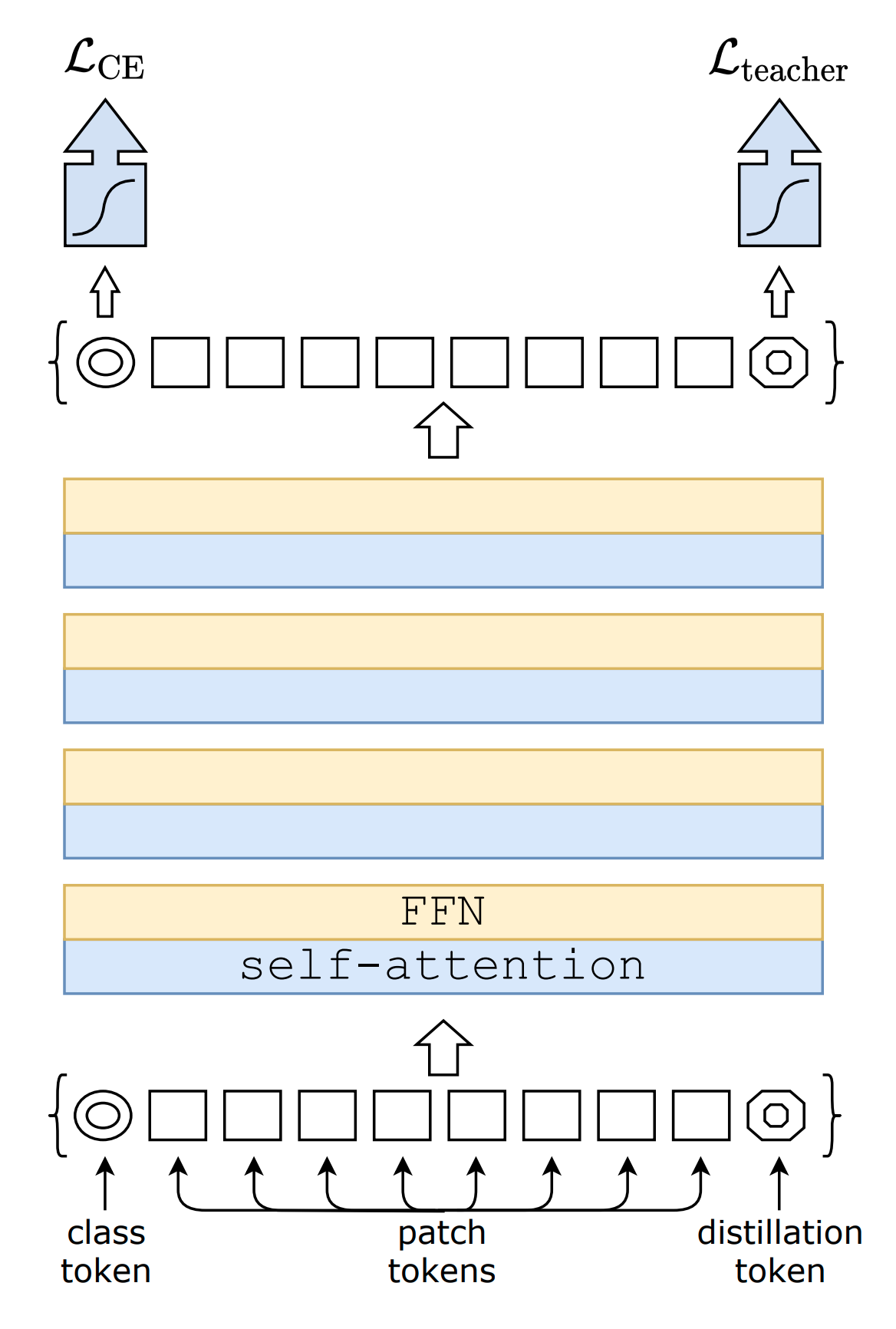
DeiT.deit_tiny_patch16_224() DeiT.deit_small_patch16_224() DeiT.deit_base_patch16_224() DeiT.deit_base_patch16_384()
- Parameters
head (nn.Module, optional) – [description]. Defaults to DeiTClassificationHead.
tokens (nn.Module, optional) – [description]. Defaults to DeiTTokens.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class glasses.models.classification.DenseNet(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.densenet.DenseNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetHead'>, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.base.ClassificationModuleImplementation of DenseNet proposed in Densely Connected Convolutional Networks
Create a default models
DenseNet.densenet121() DenseNet.densenet161() DenseNet.densenet169() DenseNet.densenet201()
Examples
# change activation DenseNet.densenet121(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) DenseNet.densenet121(n_classes=100) # pass a different block DenseNet.densenet121(block=...) # change the initial convolution model = DenseNet.densenet121() model.encoder.gate.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3) # store each feature x = torch.rand((1, 3, 224, 224)) model = DenseNet.densenet121() # first call .features, this will activate the forward hooks and tells the model you'll like to get the features model.encoder.features model(torch.randn((1,3,224,224))) # get the features from the encoder features = model.encoder.features print([x.shape for x in features]) # [torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28]), torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14]), torch.Size([1, 512, 7, 7]), torch.Size([1, 1024, 7, 7])]
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
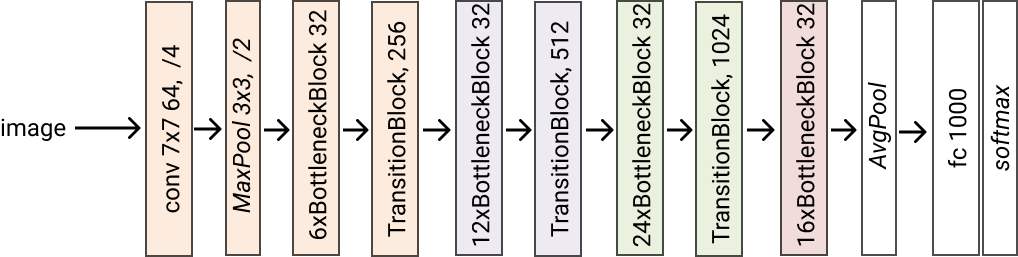
- classmethod densenet121(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.densenet.DenseNet[source]¶
Creates a densenet121 model. Grow rate is set to 32
- Returns
A densenet121 model
- Return type
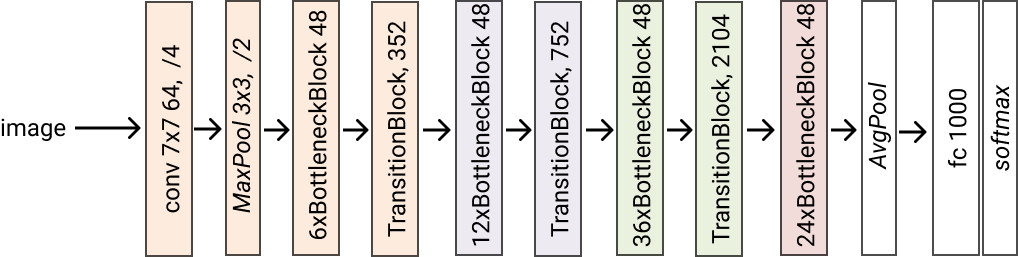
- classmethod densenet161(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.densenet.DenseNet[source]¶
Creates a densenet161 model. Grow rate is set to 48
- Returns
A densenet161 model
- Return type
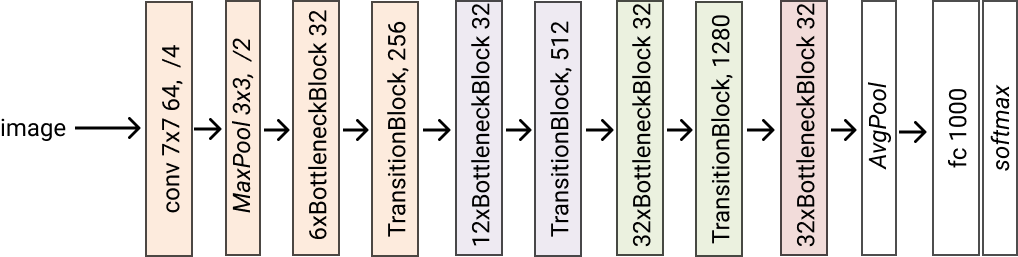
- classmethod densenet169(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.densenet.DenseNet[source]¶
Creates a densenet169 model. Grow rate is set to 32
- Returns
A densenet169 model
- Return type
- classmethod densenet201(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.densenet.DenseNet[source]¶
Creates a densenet201 model. Grow rate is set to 32
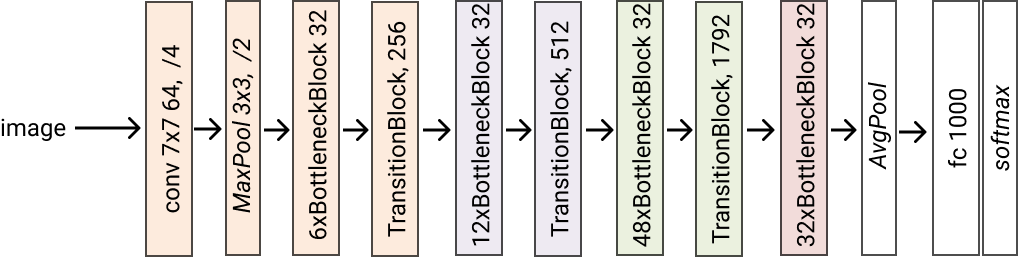
- Returns
A densenet201 model
- Return type
- forward(x: torch.Tensor) torch.Tensor[source]¶
Defines the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses.
Note
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.EfficientNet(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNetHead'>, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.base.ClassificationModuleImplementation of EfficientNet proposed in EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks

The basic architecture is similar to MobileNetV2 as was computed by using Progressive Neural Architecture Search .
The following table shows the basic architecture (EfficientNet-efficientnet_b0):

Then, the architecture is scaled up from -efficientnet_b0 to -efficientnet_b7 using compound scaling.

EfficientNet.efficientnet_b0() EfficientNet.efficientnet_b1() EfficientNet.efficientnet_b2() EfficientNet.efficientnet_b3() EfficientNet.efficientnet_b4() EfficientNet.efficientnet_b5() EfficientNet.efficientnet_b6() EfficientNet.efficientnet_b7() EfficientNet.efficientnet_b8() EfficientNet.efficientnet_l2()
Examples
EfficientNet.efficientnet_b0(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) EfficientNet.efficientnet_b0(n_classes=100) # pass a different block EfficientNet.efficientnet_b0(block=...) # store each feature x = torch.rand((1, 3, 224, 224)) model = EfficientNet.efficientnet_b0() # first call .features, this will activate the forward hooks and tells the model you'll like to get the features model.encoder.features model(torch.randn((1,3,224,224))) # get the features from the encoder features = model.encoder.features print([x.shape for x in features]) # [torch.Size([1, 32, 112, 112]), torch.Size([1, 24, 56, 56]), torch.Size([1, 40, 28, 28]), torch.Size([1, 80, 14, 14])]
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- default_depths: List[int] = [1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 1]¶
- default_widths: List[int] = [32, 16, 24, 40, 80, 112, 192, 320, 1280]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_b0(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_b1(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_b2(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_b3(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_b4(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_b5(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_b6(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_b7(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_b8(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_l2(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod from_config(config, key, *args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- models_config = {'efficientnet_b0': (1.0, 1.0, 0.2), 'efficientnet_b1': (1.0, 1.1, 0.2), 'efficientnet_b2': (1.1, 1.2, 0.3), 'efficientnet_b3': (1.2, 1.4, 0.3), 'efficientnet_b4': (1.4, 1.8, 0.4), 'efficientnet_b5': (1.6, 2.2, 0.4), 'efficientnet_b6': (1.8, 2.6, 0.5), 'efficientnet_b7': (2.0, 3.1, 0.5), 'efficientnet_b8': (2.2, 3.6, 0.5), 'efficientnet_l2': (4.3, 5.3, 0.5)}¶
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.EfficientNetLite(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNetHead'>, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNetImplementations of EfficientNetLite proposed in Higher accuracy on vision models with EfficientNet-Lite
Main differences from the EfficientNet implementation are:
Removed squeeze-and-excitation networks since they are not well supported
Replaced all swish activations with RELU6, which significantly improved the quality of post-training quantization (explained later)
Fixed the stem and head while scaling models up in order to reduce the size and computations of scaled models
Examples
Create a default model
>>> EfficientNetLite.efficientnet_lite0() >>> EfficientNetLite.efficientnet_lite1() >>> EfficientNetLite.efficientnet_lite2() >>> EfficientNetLite.efficientnet_lite3() >>> EfficientNetLite.efficientnet_lite4()
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- classmethod efficientnet_lite0(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_lite1(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_lite2(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_lite3(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod efficientnet_lite4(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- classmethod from_config(config, key, *args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- models_config = {'efficientnet_lite0': (1.0, 1.0, 0.2), 'efficientnet_lite1': (1.0, 1.1, 0.2), 'efficientnet_lite2': (1.1, 1.2, 0.3), 'efficientnet_lite3': (1.2, 1.4, 0.3), 'efficientnet_lite4': (1.4, 1.8, 0.3)}¶
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.FishNet(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.fishnet.FishNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.fishnet.FishNetHead'>, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.base.ClassificationModuleImplementation of ResNet proposed in FishNet: A Versatile Backbone for Image, Region, and Pixel Level Prediction
Honestly, this model it is very weird and it has some mistakes in the paper that nobody ever cared to correct. It is a nice idea, but it could have been described better and definitly implemented better. The author’s code is terrible, I have based mostly of my implemente on this amazing repo Fishnet-PyTorch.
The following image is taken from the paper and shows the architecture detail.
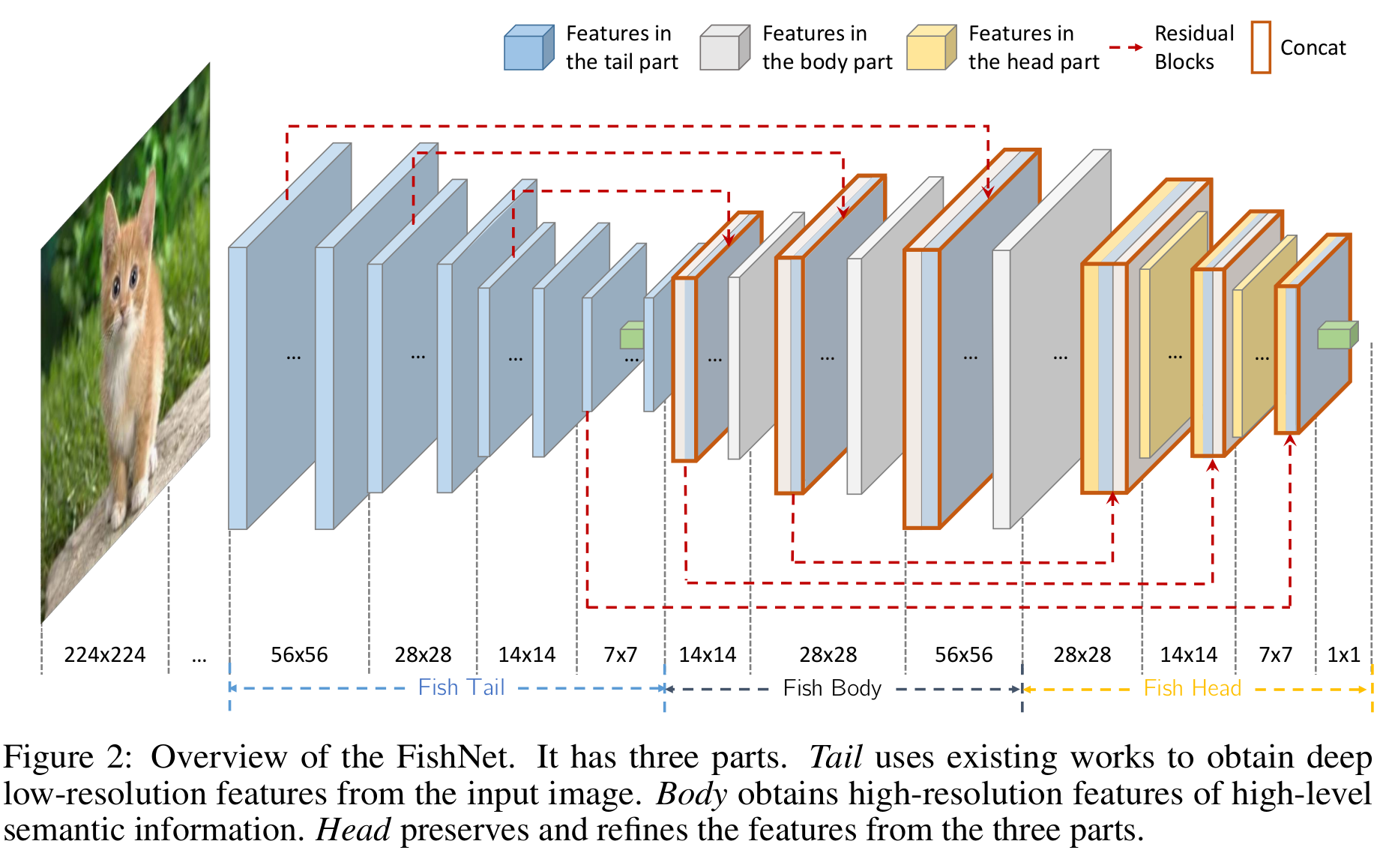
FishNet.fishnet99() FishNet.fishnet150()
Examples
FishNet.fishnet99(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) FishNet.fishnet99(n_classes=100) # pass a different block block = lambda in_ch, out_ch, **kwargs: nn.Sequential(FishNetBottleNeck(in_ch, out_ch), SpatialSE(out_ch)) FishNet.fishnet99(block=block)
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- classmethod fishnet150(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.fishnet.FishNet[source]¶
Return a fishnet150 model
- Returns
[description]
- Return type
- classmethod fishnet99(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.fishnet.FishNet[source]¶
Return a fishnet99 model
- Returns
[description]
- Return type
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.MobileNet(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNetHead'>, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNetImplementation of MobileNet v2 proposed in MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks
MobileNet is a special case of EfficientNet.
MobileNet.mobilenet_v2()
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- classmethod mobilenet_v2(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.efficientnet.EfficientNet[source]¶
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.RegNet(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = functools.partial(<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetEncoder'>, start_features=32, stem=functools.partial(<class 'glasses.nn.blocks.ConvBnAct'>, kernel_size=3, stride=2), downsample_first=True, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.regnet.RegNetXBotteneckBlock'>), *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetImplementation of RegNet proposed in Designing Network Design Spaces
The main idea is to start with a high dimensional search space and iteratively reduce the search space by empirically apply constrains based on the best performing models sampled by the current search space.
The resulting models are light, accurate, and faster than EfficientNets (up to 5x times!)
For example, to go from \(AnyNet_A\) to \(AnyNet_B\) they fixed the bottleneck ratio \(b_i\) for all stage \(i\). The following table shows all the restrictions applied from one search space to the next one.
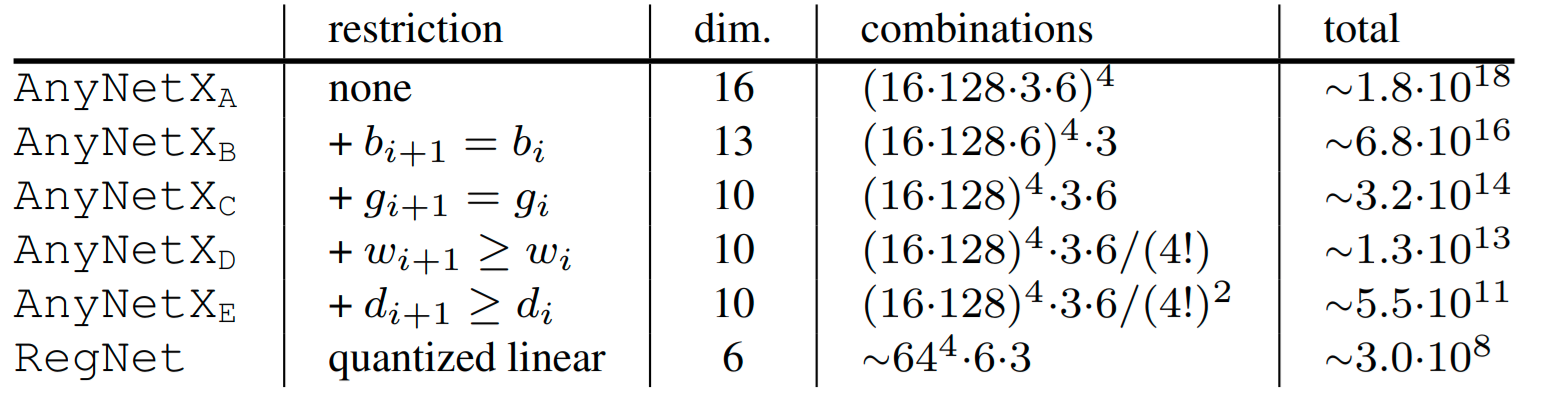
The paper is really well written and very interesting, I highly recommended read it.
ResNet.regnetx_002() ResNet.regnetx_004() ResNet.regnetx_006() ResNet.regnetx_008() ResNet.regnetx_016() ResNet.regnetx_040() ResNet.regnetx_064() ResNet.regnetx_080() ResNet.regnetx_120() ResNet.regnetx_160() ResNet.regnetx_320() # Y variants (with SE) ResNet.regnety_002() # ... ResNet.regnetx_320() You can easily customize your model
Examples
# change activation RegNet.regnetx_004(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) RegNet.regnetx_004(n_classes=100) # pass a different block RegNet.regnetx_004(block=RegNetYBotteneckBlock) # change the steam model = RegNet.regnetx_004(stem=ResNetStemC) change shortcut model = RegNet.regnetx_004(block=partial(RegNetYBotteneckBlock, shortcut=ResNetShorcutD)) # store each feature x = torch.rand((1, 3, 224, 224)) # get features model = RegNet.regnetx_004() # first call .features, this will activate the forward hooks and tells the model you'll like to get the features model.encoder.features model(torch.randn((1,3,224,224))) # get the features from the encoder features = model.encoder.features print([x.shape for x in features]) #[torch.Size([1, 32, 112, 112]), torch.Size([1, 32, 56, 56]), torch.Size([1, 64, 28, 28]), torch.Size([1, 160, 14, 14])]
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- models_config = {'regnetx_002': ([1, 1, 4, 7], [24, 56, 152, 368], 8), 'regnetx_004': ([1, 2, 7, 12], [32, 64, 160, 384], 16), 'regnetx_006': ([1, 3, 5, 7], [48, 96, 240, 528], 24), 'regnetx_008': ([1, 3, 7, 5], [64, 128, 288, 672], 16), 'regnetx_016': ([2, 4, 10, 2], [72, 168, 408, 912], 24), 'regnetx_032': ([2, 6, 15, 2], [96, 192, 432, 1008], 48), 'regnetx_040': ([2, 5, 14, 2], [80, 240, 560, 1360], 40), 'regnetx_064': ([2, 4, 10, 1], [168, 392, 784, 1624], 56), 'regnetx_080': ([2, 5, 15, 1], [80, 240, 720, 1920], 80), 'regnetx_120': ([2, 5, 11, 1], [224, 448, 896, 2240], 112), 'regnetx_160': ([2, 6, 13, 1], [256, 512, 896, 2048], 128), 'regnetx_320': ([2, 7, 13, 1], [336, 672, 1344, 2520], 168), 'regnety_002': ([1, 1, 4, 7], [24, 56, 152, 368], 8), 'regnety_004': ([1, 3, 6, 6], [48, 104, 208, 440], 8), 'regnety_006': ([1, 3, 7, 4], [48, 112, 256, 608], 16), 'regnety_008': ([1, 3, 8, 2], [64, 128, 320, 768], 16), 'regnety_016': ([2, 6, 17, 2], [48, 120, 336, 888], 24), 'regnety_032': ([2, 5, 13, 1], [72, 216, 576, 1512], 24), 'regnety_040': ([2, 6, 12, 2], [128, 192, 512, 1088], 64), 'regnety_064': ([2, 7, 14, 2], [144, 288, 576, 1296], 72), 'regnety_080': ([2, 4, 10, 1], [168, 448, 896, 2016], 56), 'regnety_120': ([2, 5, 11, 1], [224, 448, 896, 2240], 112), 'regnety_160': ([2, 4, 11, 1], [224, 448, 1232, 3024], 112), 'regnety_320': ([2, 5, 12, 1], [232, 696, 1392, 3712], 232)}¶
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.ResNeSt(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeStEncoder'>, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetImplementation of ResNeSt proposed in “ResNeSt: Split-Attention Networks”.
This model beats EfficientNet both in speed and accuracy.
ResNeSt.resnest14d() ResNeSt.resnest26d() ResNeSt.resnest50d() ResNeSt.resnest50d_1s4x24d() ResNeSt.resnest50d_4s2x40d() # 'e' models have a bigger start_features (128), resulting in a 64 stem width ResNeSt.resnest101e() ResNeSt.resnest200e() ResNeSt.resnest269e() # create a ResNeSt50_2s4s40d ResNeSt.resnet50d(radix=2, groups=4, base_width=80)
Examples
# change activation ResNeSt.resnest50d(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) ResNeSt.resnest50d(n_classes=100) # pass a different block ResNeSt.resnest50d(block=SENetBasicBlock) # store each feature x = torch.rand((1, 3, 224, 224)) model = ResNeSt.resnest50d() # first call .features, this will activate the forward hooks and tells the model you'll like to get the features model.encoder.features model(torch.randn((1,3,224,224))) # get the features from the encoder features = model.encoder.features print([x.shape for x in features]) #[torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112]), torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56]), torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28]), torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14])]
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- classmethod resnest101e(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeSt[source]¶
- classmethod resnest14d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeSt[source]¶
- classmethod resnest200e(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeSt[source]¶
- classmethod resnest269e(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeSt[source]¶
- classmethod resnest26d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeSt[source]¶
- classmethod resnest50d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeSt[source]¶
- classmethod resnest50d_1s4x24d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeSt[source]¶
- classmethod resnest50d_4s2x40d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeSt[source]¶
- classmethod resnest50d_fast(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnest.ResNeSt[source]¶
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.ResNet(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetHead'>, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.base.ClassificationModuleImplementation of ResNet proposed in Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
ResNet.resnet18() ResNet.resnet26() ResNet.resnet34() ResNet.resnet50() ResNet.resnet101() ResNet.resnet152() ResNet.resnet200() Variants (d) proposed in `Bag of Tricks for Image Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.01187.pdf>`_ ResNet.resnet26d() ResNet.resnet34d() ResNet.resnet50d() # You can construct your own one by chaning `stem` and `block` resnet101d = ResNet.resnet101(stem=ResNetStemC, block=partial(ResNetBottleneckBlock, shortcut=ResNetShorcutD))
Examples
# change activation ResNet.resnet18(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) ResNet.resnet18(n_classes=100) # pass a different block ResNet.resnet18(block=SENetBasicBlock) # change the steam model = ResNet.resnet18(stem=ResNetStemC) change shortcut model = ResNet.resnet18(block=partial(ResNetBasicBlock, shortcut=ResNetShorcutD)) # store each feature x = torch.rand((1, 3, 224, 224)) # get features model = ResNet.resnet18() # first call .features, this will activate the forward hooks and tells the model you'll like to get the features model.encoder.features model(torch.randn((1,3,224,224))) # get the features from the encoder features = model.encoder.features print([x.shape for x in features]) #[torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112]), torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56]), torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28]), torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14])]
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- classmethod resnet101(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBottleneckBlock'>, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNet[source]¶
Creates a resnet101 model
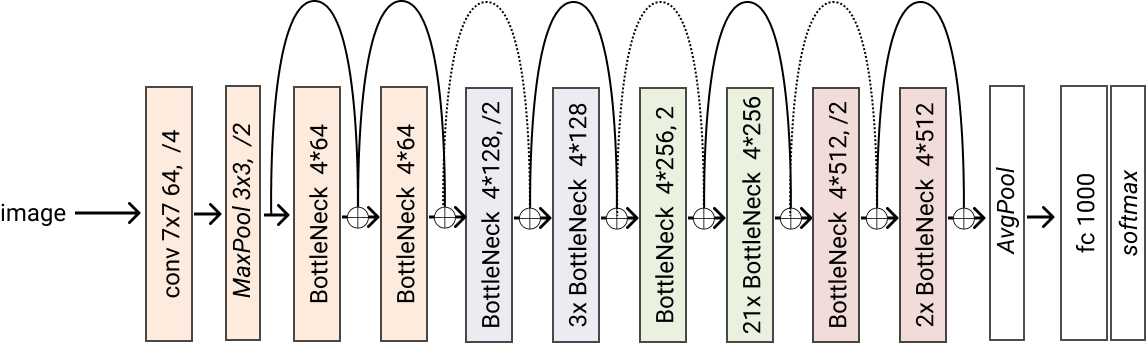
- Returns
A resnet101 model
- Return type
- classmethod resnet152(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBottleneckBlock'>, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNet[source]¶
Creates a resnet152 model
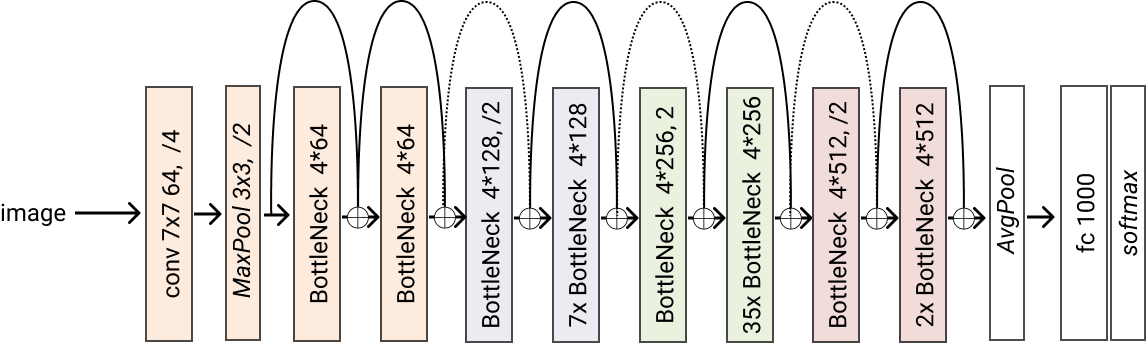
- Returns
A resnet152 model
- Return type
- classmethod resnet18(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBasicBlock'>, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNet[source]¶
Creates a resnet18 model
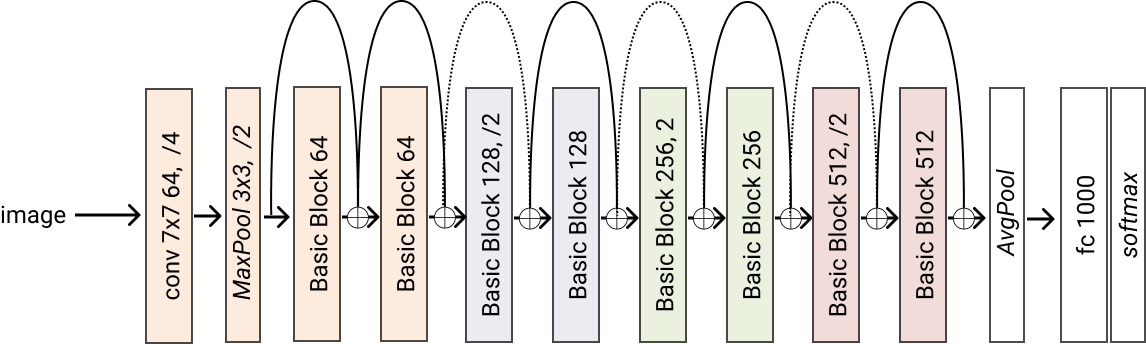
- Returns
A resnet18 model
- Return type
- classmethod resnet200(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBottleneckBlock'>, **kwargs)[source]¶
Creates a resnet200 model
- Returns
A resnet200 model
- Return type
- classmethod resnet26(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBottleneckBlock'>, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNet[source]¶
Creates a resnet26 model
- Returns
A resnet26 model
- Return type
- classmethod resnet26d(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBottleneckBlock'>, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNet[source]¶
Creates a resnet26d model
- Returns
A resnet26d model
- Return type
- classmethod resnet34(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBasicBlock'>, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNet[source]¶
Creates a resnet34 model
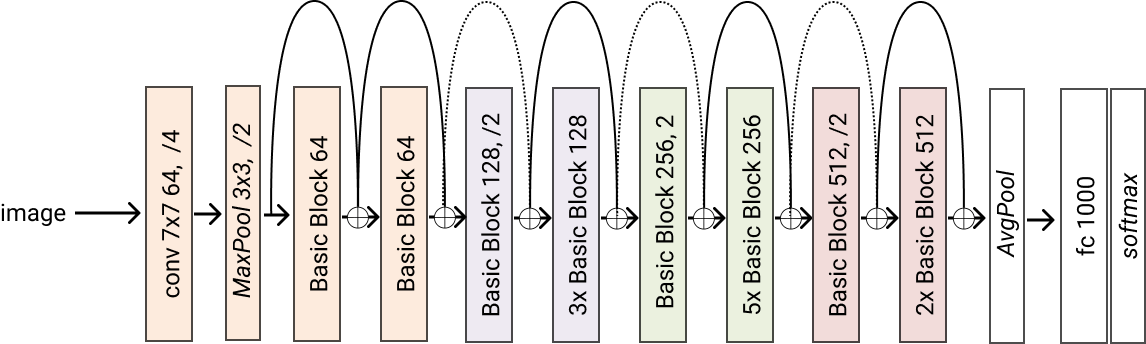
- Returns
A resnet34 model
- Return type
- classmethod resnet34d(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBasicBlock'>, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNet[source]¶
Creates a resnet34 model

- Returns
A resnet34 model
- Return type
- classmethod resnet50(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBottleneckBlock'>, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNet[source]¶
Creates a resnet50 model
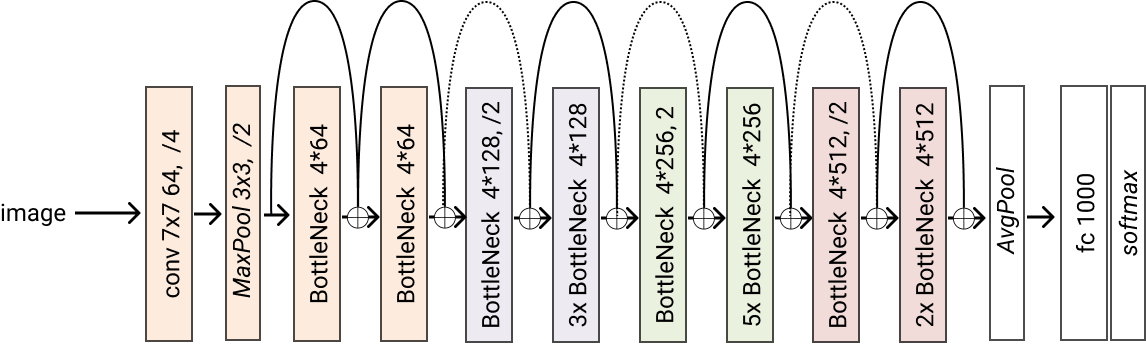
- Returns
A resnet50 model
- Return type
- classmethod resnet50d(*args, block=<class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetBottleneckBlock'>, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNet[source]¶
Creates a resnet50d model

- Returns
A resnet50d model
- Return type
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.ResNetXt(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetHead'>, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetImplementation of ResNetXt proposed in “Aggregated Residual Transformation for Deep Neural Networks”
Create a default model
ResNetXt.resnext50_32x4d() ResNetXt.resnext101_32x8d() # create a resnetxt18_32x4d ResNetXt.resnet18(block=ResNetXtBottleNeckBlock, groups=32, base_width=4)
Examples
# change activation ResNetXt.resnext50_32x4d(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) ResNetXt.resnext50_32x4d(n_classes=100) # pass a different block ResNetXt.resnext50_32x4d(block=SENetBasicBlock) # change the initial convolution model = ResNetXt.resnext50_32x4d model.encoder.gate.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3) # store each feature x = torch.rand((1, 3, 224, 224)) model = ResNetXt.resnext50_32x4d() # first call .features, this will activate the forward hooks and tells the model you'll like to get the features model.encoder.features model(torch.randn((1,3,224,224))) # get the features from the encoder features = model.encoder.features print([x.shape for x in features]) #[torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112]), torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56]), torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28]), torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14])]
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- classmethod resnext101_32x16d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnetxt.ResNetXt[source]¶
Creates a resnext101_32x16d model
- Returns
A resnext101_32x16d model
- Return type
- classmethod resnext101_32x32d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnetxt.ResNetXt[source]¶
Creates a resnext101_32x32d model
- Returns
A resnext101_32x32d model
- Return type
- classmethod resnext101_32x48d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnetxt.ResNetXt[source]¶
Creates a resnext101_32x48d model
- Returns
A resnext101_32x48d model
- Return type
- classmethod resnext101_32x8d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnetxt.ResNetXt[source]¶
Creates a resnext101_32x8d model
- Returns
A resnext101_32x8d model
- Return type
- classmethod resnext50_32x4d(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.resnetxt.ResNetXt[source]¶
Creates a resnext50_32x4d model
- Returns
A resnext50_32x4d model
- Return type
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.SEResNet(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetHead'>, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetImplementation of Squeeze and Excitation ResNet using booth the original spatial se and the channel se proposed in Concurrent Spatial and Channel ‘Squeeze & Excitation’ in Fully Convolutional Networks The models with the channel se are labeldb with prefix c
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- classmethod se_resnet101(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.senet.SEResNet[source]¶
Original SE resnet101 with Spatial Squeeze and Excitation
- Returns
[description]
- Return type
- classmethod se_resnet152(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.senet.SEResNet[source]¶
Original SE resnet152 with Spatial Squeeze and Excitation
- Returns
[description]
- Return type
- classmethod se_resnet18(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.senet.SEResNet[source]¶
Original SE resnet18 with Spatial Squeeze and Excitation
- Returns
[description]
- Return type
- classmethod se_resnet34(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.senet.SEResNet[source]¶
Original SE resnet34 with Spatial Squeeze and Excitation
- Returns
[description]
- Return type
- classmethod se_resnet50(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.senet.SEResNet[source]¶
Original SE resnet50 with Spatial Squeeze and Excitation
- Returns
[description]
- Return type
- training: bool¶
- class glasses.models.classification.VGG(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGGEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGGHead'>, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.base.ClassificationModuleImplementation of VGG proposed in Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition
VGG.vgg11() VGG.vgg13() VGG.vgg16() VGG.vgg19() VGG.vgg11_bn() VGG.vgg13_bn() VGG.vgg16_bn() VGG.vgg19_bn()
Please be aware that the bn models uses BatchNorm but they are very old and people back then don’t know the bias is superfluous in a conv followed by a batchnorm.
Examples
# change activation VGG.vgg11(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) VGG.vgg11(n_classes=100) # pass a different block from nn.models.classification.senet import SENetBasicBlock VGG.vgg11(block=SENetBasicBlock) # store the features tensor after every block
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- training: bool¶
- classmethod vgg11(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGG[source]¶
Creates a vgg11 model
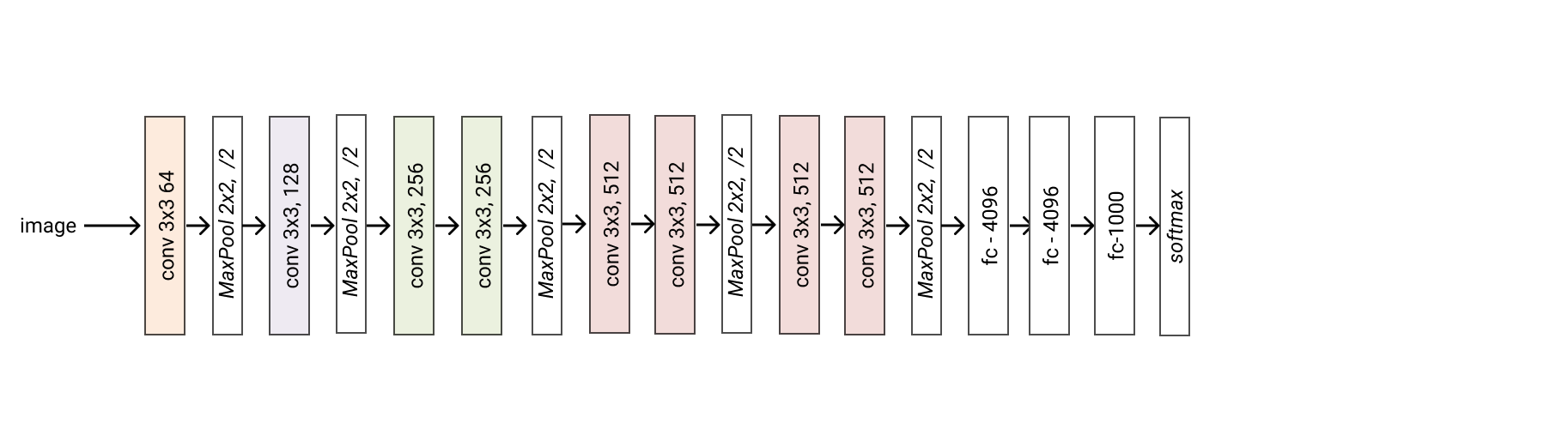
- Returns
A vgg11 model
- Return type
- classmethod vgg11_bn(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGG[source]¶
Creates a vgg11 model with batchnorm
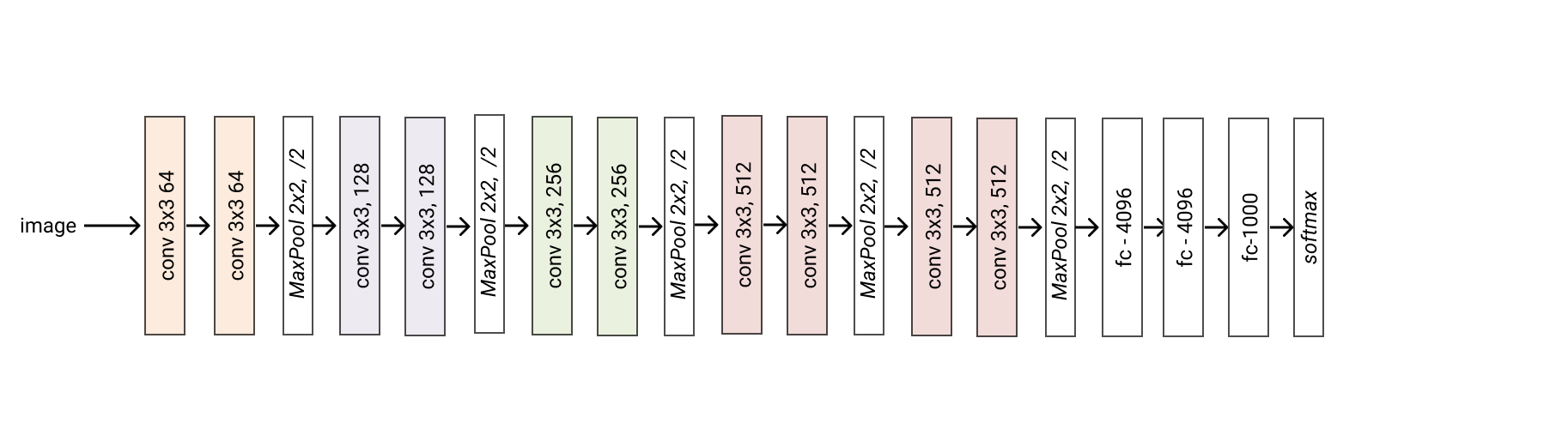
- Returns
A vgg13 model
- Return type
- classmethod vgg13(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGG[source]¶
Creates a vgg13 model

- Returns
A vgg13 model
- Return type
- classmethod vgg13_bn(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGG[source]¶
Creates a vgg13 model with batchnorm

- Returns
A vgg13 model
- Return type
- classmethod vgg16(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGG[source]¶
Creates a vgg16 model
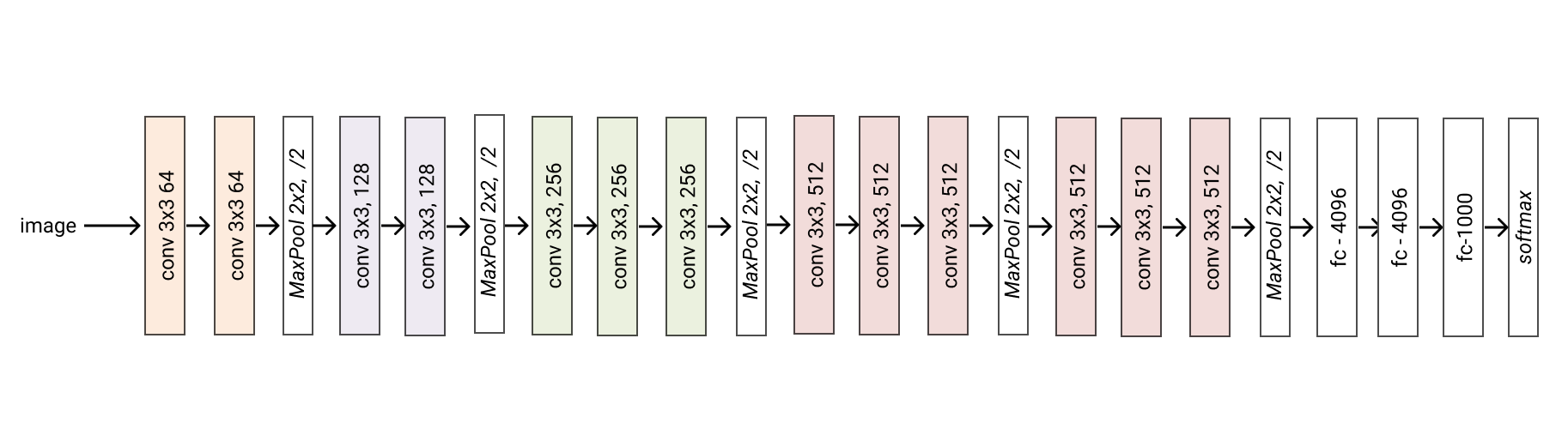
- Returns
A vgg16 model
- Return type
- classmethod vgg16_bn(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGG[source]¶
Creates a vgg16 model with batchnorm

- Returns
A vgg16 model
- Return type
- classmethod vgg19(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGG[source]¶
Creates a vgg19 model
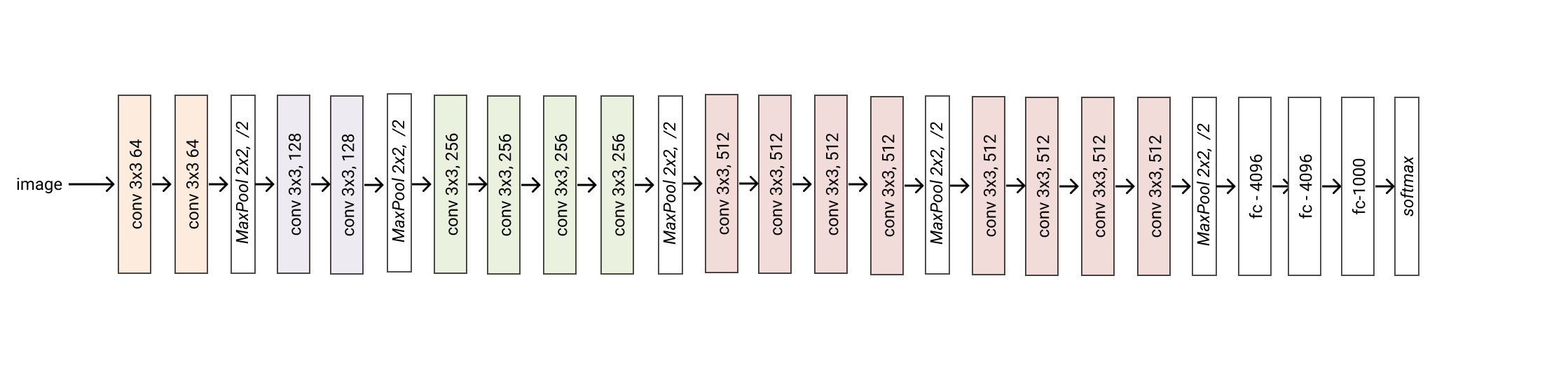
- Returns
A vgg19 model
- Return type
- classmethod vgg19_bn(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.vgg.VGG[source]¶
Creates a vgg19 model with batchnorm

- Returns
A vgg19 model
- Return type
- class glasses.models.classification.ViT(embedding: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.vit.PatchEmbedding'>, encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.vit.TransformerEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.vit.ViTClassificationHead'>, in_channels: int = 3, patch_size: int = 16, emb_size: int = 768, img_size: int = 224, tokens: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.vit.ViTTokens'>, depth: int = 12, n_classes: int = 1000, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
torch.nn.modules.container.Sequential,glasses.models.base.VisionModuleImplementation of Vision Transformer (ViT) proposed in An Image Is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers For Image Recognition At Scale
The following image from the authors shows the architecture.

ViT.vit_small_patch16_224() ViT.vit_base_patch16_224() ViT.vit_base_patch16_384() ViT.vit_base_patch32_384() ViT.vit_huge_patch16_224() ViT.vit_huge_patch32_384() ViT.vit_large_patch16_224() ViT.vit_large_patch16_384() ViT.vit_large_patch32_384()
Examples
# change activation ViT.vit_base_patch16_224(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) ViT.vit_base_patch16_224(n_classes=100) # pass a different block, default is TransformerEncoderBlock ViT.vit_base_patch16_224(block=MyCoolTransformerBlock) # get features model = ViT.vit_base_patch16_224 # first call .features, this will activate the forward hooks and tells the model you'll like to get the features model.encoder.features model(torch.randn((1,3,224,224))) # get the features from the encoder features = model.encoder.features print([x.shape for x in features]) #[[torch.Size([1, 197, 768]), torch.Size([1, 197, 768]), ...] # change the tokens, you have to subclass ViTTokens class MyTokens(ViTTokens): def __init__(self, emb_size: int): super().__init__(emb_size) self.my_new_token = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, 1, emb_size)) ViT(tokens=MyTokens)
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – [description]. Defaults to 3.
patch_size (int, optional) – [description]. Defaults to 16.
emb_size (int, optional) – Embedding dimensions Defaults to 768.
img_size (int, optional) – [description]. Defaults to 224.
tokens (nn.Module, optional) – A module that contains the tokens as his parameters. Defaults to ViTTokens.
depth (int, optional) – [description]. Defaults to 12.
n_classes (int, optional) – [description]. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- class glasses.models.classification.WideResNet(encoder: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetEncoder'>, head: torch.nn.modules.module.Module = <class 'glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetHead'>, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
glasses.models.classification.resnet.ResNetImplementation of Wide ResNet proposed in “Wide Residual Networks”
Create a default model
WideResNet.wide_resnet50_2() WideResNet.wide_resnet101_2() # create a wide_resnet18_4 WideResNet.resnet18(block=WideResNetBottleNeckBlock, width_factor=4)
Examples
# change activation WideResNet.resnext50_32x4d(activation = nn.SELU) # change number of classes (default is 1000 ) WideResNet.resnext50_32x4d(n_classes=100) # pass a different block WideResNet.resnext50_32x4d(block=SENetBasicBlock) # change the initial convolution model = WideResNet.resnext50_32x4d model.encoder.gate.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3) # store each feature x = torch.rand((1, 3, 224, 224)) model = WideResNet.wide_resnet50_2() features = [] x = model.encoder.gate(x) for block in model.encoder.layers: x = block(x) features.append(x) print([x.shape for x in features]) # [torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56]), torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28]), torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14]), torch.Size([1, 512, 7, 7])]
- Parameters
in_channels (int, optional) – Number of channels in the input Image (3 for RGB and 1 for Gray). Defaults to 3.
n_classes (int, optional) – Number of classes. Defaults to 1000.
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- training: bool¶
- classmethod wide_resnet101_2(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.wide_resnet.WideResNet[source]¶
Creates a wide_resnet50_2 model
- Returns
A wide_resnet50_2 model
- Return type
- classmethod wide_resnet50_2(*args, **kwargs) glasses.models.classification.wide_resnet.WideResNet[source]¶
Creates a wide_resnet50_2 model
- Returns
A wide_resnet50_2 model
- Return type